In Greek mythology, Phobos is the god of fear. Phobos is fear personified and represents a feeling rather than a being. Phobos is also depicted on the shields of heroes as they go into battle, representing his frequent participation in wars.
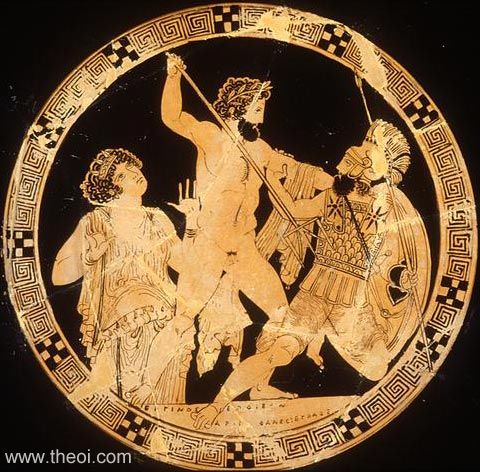
Ares, the god of war, is the father of Phobos. Phobos has a twin brother, Deimos, who is the god of terror. Deimos and Phobos are often pictured together because they represent similar feelings. Phobos and Deimos are often called upon to aid Ares during battle because of the feelings they invoke upon their enemies.
Phobos is sometimes illustrated as a young boy with a lion’s head. Phobos is also illustrated in the shield of Agamemnon as being in the center of the shield with Phobo having a lion’s head.
Phobos in War
 In Sparta, Phobos was worshipped because he was the son of Ares and invoked fear into the enemies of Spartans. If sacrifices were made during battle, they would be made in the name of Phobos to honor him. Phobos and Deimos are frequently seen driving the chariot of Ares, representing their alliance with their father in battle.
In Sparta, Phobos was worshipped because he was the son of Ares and invoked fear into the enemies of Spartans. If sacrifices were made during battle, they would be made in the name of Phobos to honor him. Phobos and Deimos are frequently seen driving the chariot of Ares, representing their alliance with their father in battle.
In addition to his father, Ares, and his brother, Deimos, Phobos also accompanies the following alliances in war:
- The Keres (death spirits)
- Proioxis
- Homados
- Palioxis
- Androktasiai
- Kydoimos
Phobos in The Iliad and Shield of Hercules
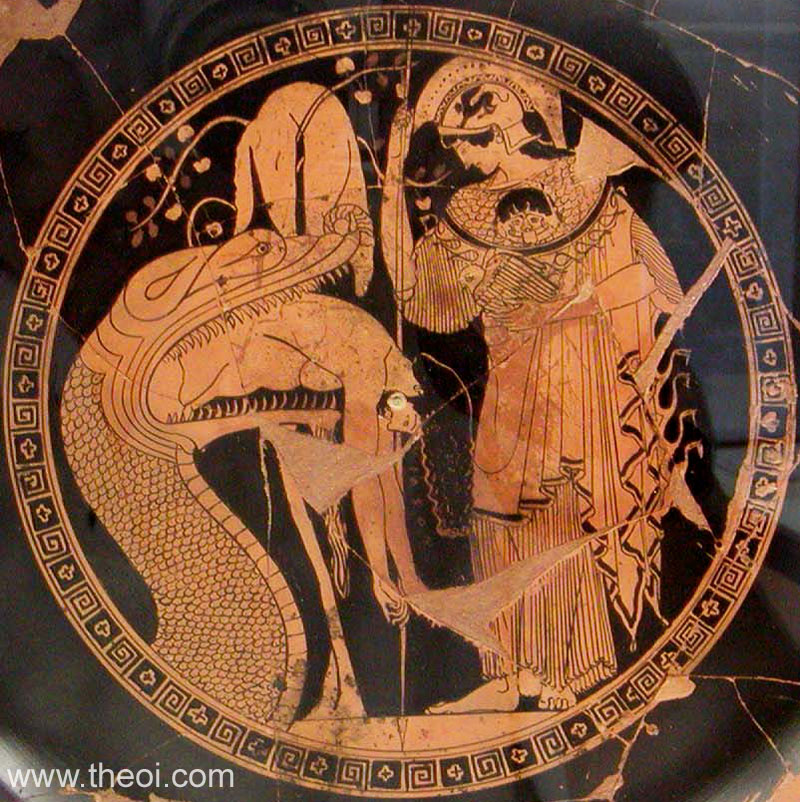
Homer brings mention to Phobos in The Iliad many times. Phobos is described as joining his brother, Deimos, and sister, Eris, in driving Ares in his chariot. Another mention of Phobos in The Iliad describes Athena holding an aegis that is decorated with Phobos and his siblings. This shield encompasses the siblings of Phobos because each sibling is similar to one another. Phobos is the god of fear, Eris is the goddess of discord, and Deimos is the god of terror. The shield also contains Alke and Ioce. Alke represents extreme strength, and Ioce represents onslaught.
Homer mentions that Ares describes Phobos as his “beloved son,” who is alongside him as he walks into war. Homer describes Phobos as bringing fear even to the most patient, wise warrior.
In Hesiod’s description of Hercules’s shield, he describes the shield as having Phobos with eyes that glowed fire with a mouth of bright white teeth that showed as he stared down his opponents.
Phobos in Psychology and Astronomy
In psychology, the word phobia means to have an extreme fear of something. Phobia is derived from Phobos, which is the Greek god of fear, as well as the Greek word for fear.
In astronomy, Phobos has a very distinct place. The planet Mars, which is also the Roman god of war equivalent to Ares, has two moons. These two moons are Phobos and Deimos. Both moons were discovered in 1877, but Phobos is the larger one and the one closer to Mars. This is parallel to the myth that Phobos was closer to Ares and considered Phobos, his beloved son.
Conclusion
The father of Phobos is Ares, the god of war. Phobos had a twin brother, Deimos, who is the god of terror. Phobos is considered to be Ares’s beloved son. Phobos and Deimos would accompany Ares in war, often driving the chariot that Ares would ride in.
Today, Phobos has psychological and astronomical ties. Phobos means “fear” in Greek, and it is where the English word phobia is derived, as phobia means to have an extreme fear of something.
In astronomy, Phobos is the name of the largest and closest of the two moons that orbit the planet Mars. Mars is the Roman name of Ares, the god of war. As Phobos is considered to be Ares’s beloved son, it is only appropriate that Ares would be the bigger and nearer moon to Mars.